Pumps
Selecting the Right Chemical Transfer Pump
Factors to Consider
Chemical Compatibility
Ensure the pump materials are compatible with the chemicals being transferred to prevent corrosion and leaks.
Flow Rate & Pressure
Determine the required flow rate and pressure to meet your application needs.
Safety & Regulations
Comply with industry standards and safety protocols to protect workers and the environment.
Types of Chemical Transfer Pumps
Positive Displacement
Pumps that rely on the physical movement of parts to displace fluid.
Centrifugal
Pumps that use rotational force to move fluids through an impeller.
Diaphragm
Pumps that use a flexible diaphragm to create suction and discharge.
Peristaltic
Pumps that use rollers to squeeze fluid through a flexible tube.
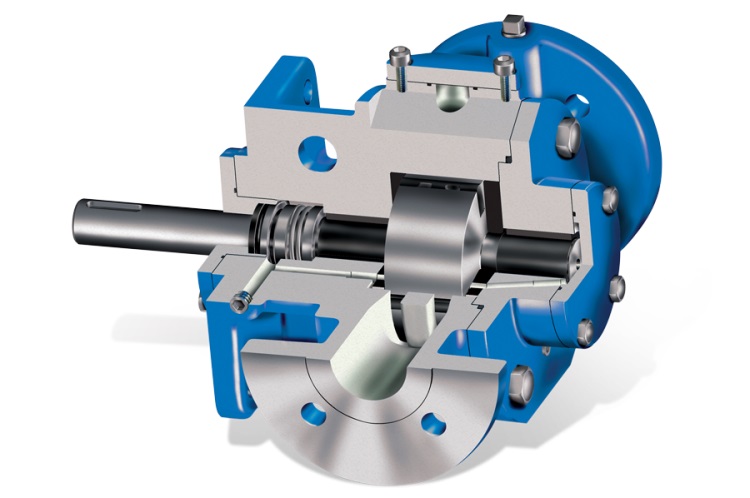
Positive Displacement Pumps
Gear Pumps
Two gears that mesh to move fluid through the pump.
Lobe Pumps
Two rotating lobes that create suction and discharge.
Piston Pumps
Use a piston to draw in and expel fluid through the pump.
Centrifugal Pumps
Impeller Design
The impeller shape and materials affect the pump’s performance and durability.
Self-Priming
Some centrifugal pumps can automatically re-prime, reducing the need for manual intervention.
Corrosion Resistance
Careful material selection is crucial to prevent corrosion in chemical applications.
Pump Materials & Compatibility
Stainless Steel
Excellent corrosion resistance for a wide range of chemicals.
Plastic
Lightweight and cost-effective for certain non-corrosive chemicals.
Specialized Alloys
Tailored for highly aggressive chemicals or extreme temperatures.
Elastomers
Flexible components to seal and protect against leaks.
Flow Rate & Pressure Requirements
Determine Needs
Assess the required flow rate and pressure for your applications.
Select Appropriate Pump
Choose a pump that meets or exceeds your performance requirements.
Verify Compatibility
Ensure the pump materials are suitable for the chemicals being transferred.
Maintenance & Safety
Regular inspections, cleaning, and replacement of worn components are essential for reliable and safe operation.
- Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Follow industry guidelines and safety regulations
- Implement emergency response plans for spills or leaks