Pumps
Introduction to Progressive Cavity Pumps
Introduction to Progressive Cavity Pumps
Progressive cavity pumps are a unique type of positive displacement pump used to efficiently transport a wide range of fluids, from thick slurries to low-viscosity liquids.
They operate on a simple yet effective helical screw principle, making them a versatile and reliable choice for many industrial applications.
Principle of Operation
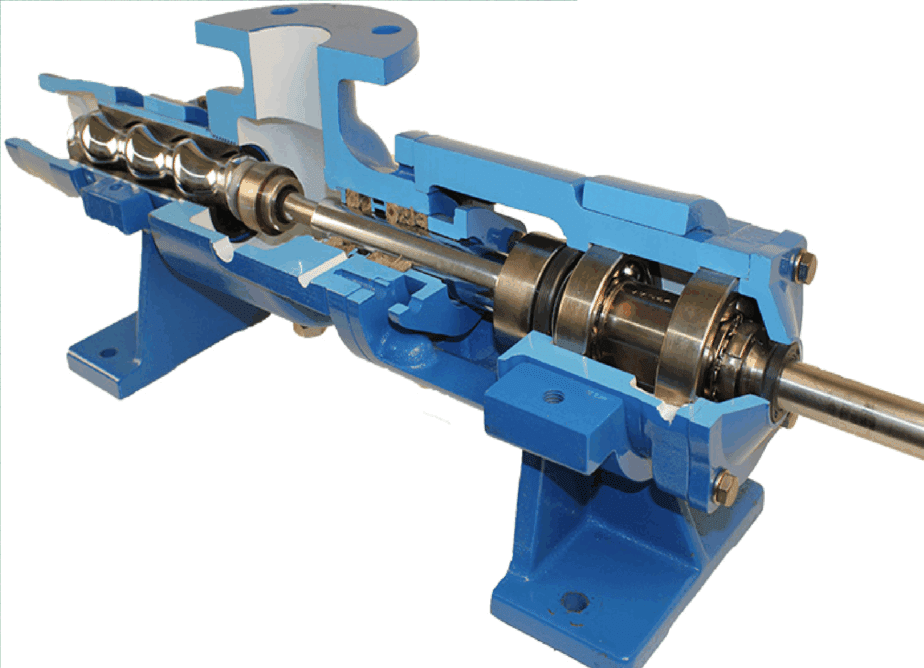
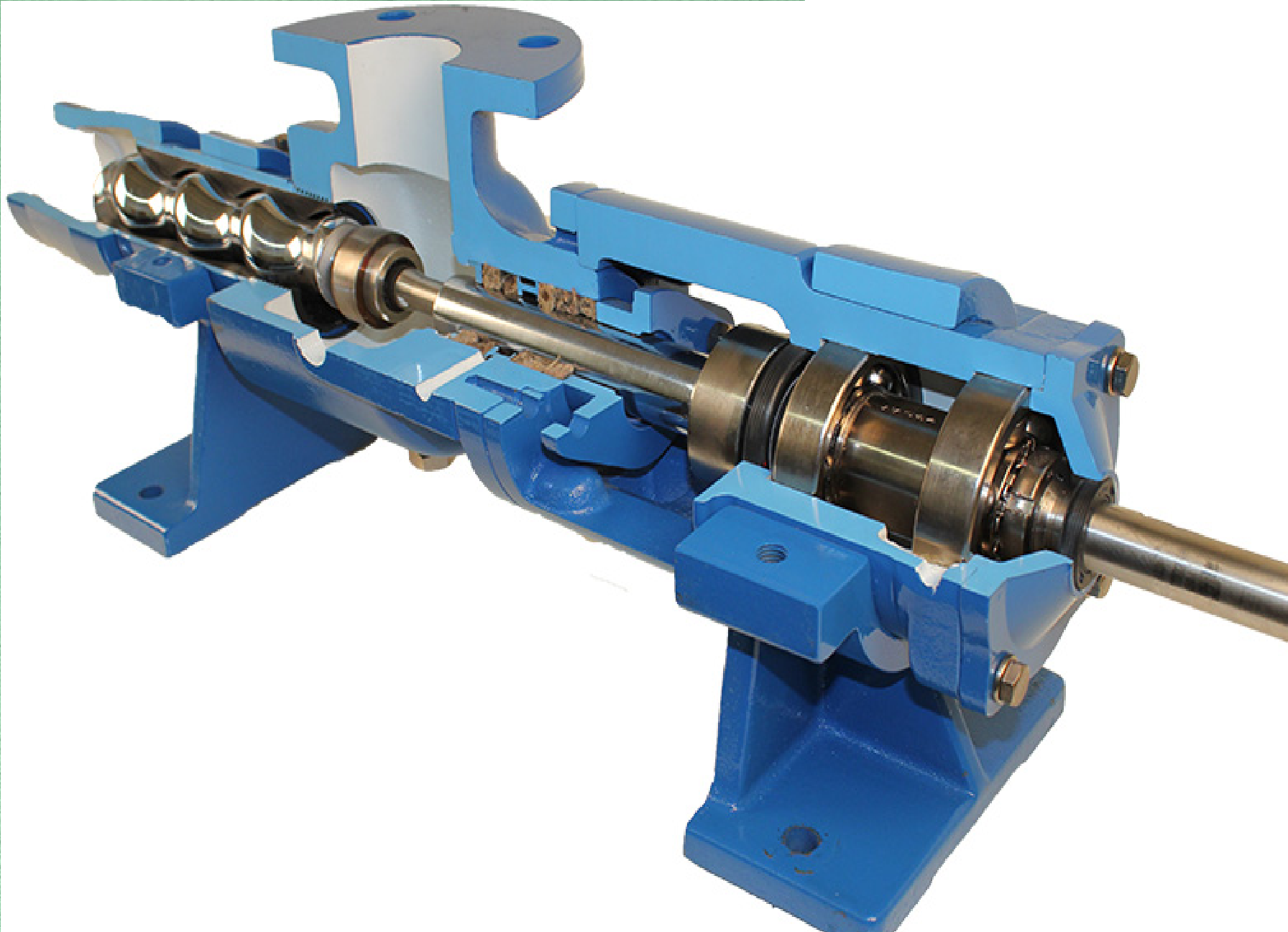
Rotor
A single-helix rotor revolves eccentrically inside a double-helix stator.
Stator
The fixed stator has an internal double-helix cavity that matches the rotor’s shape.
Pumping Action
As the rotor turns, it creates a series of sealed cavities that progressively move from the pump inlet to the outlet, drawing in and discharging the fluid.
Key Components of a Progressive Cavity Pump
Rotor
The single-helix rotor is the heart of the pump, responsible for the unique pumping action.
Stator
The double-helix stator creates the sealed cavities that trap and move the fluid.
Drive Mechanism
The rotor is typically driven by an electric motor or diesel engine, providing the necessary torque.
Advantages of Progressive Cavity Pumps
Gentle Pumping Action
The progressive cavity design minimises shear stress, making it suitable for delicate or shear-sensitive fluids.
Versatile Fluid Handling
Can handle a wide range of viscosities, from thin liquids to thick, abrasive slurries.
Self-Priming Capability
The pumps can start up with an empty suction line, making them ideal for applications with varying liquid levels.
Reversible Operation
The flow direction can be reversed, allowing the pumps to be used for both loading and unloading applications.
Applications of Progressive Cavity Pumps
Food and Beverage
Handling viscous fluids like chocolate, honey, and fruit purees with minimal product degradation.
Oil and Gas
Transferring crude oil, drilling muds, and other oilfield fluids, including high-solids content slurries.
Water and Wastewater
Pumping sludges, sewage, and other waste fluids with high solids content.
Mining and Minerals
handling abrasive, high-viscosity slurries of ore, minerals, and other mining by-products.

Maintenance and Servicing of Progressive Cavity Pumps
Inspection
Regularly check for wear on the rotor and stator, and monitor performance indicators.
Lubrication
Ensure proper lubrication of the drive mechanism and other moving parts to reduce wear.
Replacement
Replace the rotor and stator when they show significant wear to maintain optimal efficiency.
Factors Affecting Progressive Cavity Pump Performance
Fluid Viscosity
Higher viscosity fluids require more torque to pump, affecting efficiency and flow rate.
Fluid Temperature
Changes in temperature can alter the viscosity and affect the pump’s performance.
Solids Content
Abrasive solids in the fluid can accelerate wear on the rotor stator.
Discharge Pressure
High discharge pressures increase the load on the drive mechanism and reduce flow rate.
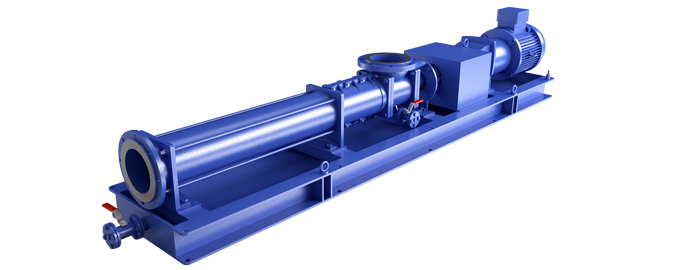
Conclusion and Summary
Progressive cavity pumps are a versatile and reliable choice for a wide range of fluid-handling applications, from thick slurries to delicate liquids. Their unique helical screw design allows for gentle, efficient, and reversible pumping, making them a valuable asset in various industries.