Pumps
Understanding the Pump Duty Point
Understanding the Pump Duty Point
The pump duty point is the specific operating condition where a pump performs most efficiently, delivering the desired flow rate and pressure. It represents the intersection of the pump’s performance curve and the system’s resistance curve, ensuring optimal pump operation.
Understanding Pump Performance Curves
Pump performance curves graphically depict a pump’s behaviour, showing how flow rate, head, efficiency, and power consumption change as the pump operates under different conditions. These curves are essential for selecting the right pump for a given application.
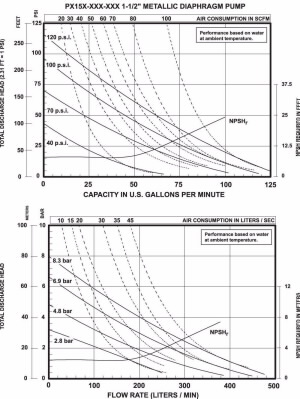
Defining the Pump Duty Point
Flow Rate
The pump duty point specifies the desired flow rate the pump must deliver to meet system requirements.
Pressure
It also defines the pressure the pump must generate to overcome the system’s resistance, such as pipe friction and elevation changes.
Efficiency
The duty point corresponds to the point on the pump’s performance curve where efficiency is maximized, ensuring optimal energy usage.
Factors Affecting the Pump Duty Point
System Resistance
Changes in pipe size, length, or fittings can alter the system resistance curve, shifting the duty point
Fluid Properties
Viscosity, density, and temperature of the pumped fluid can impact the pump’s performance and duty point.
Impeller Wear
As the impeller wears over time, the pump’s performance curve and duty point may change.
Operating Conditions
Variations in speed, suction pressure, and other operating parameters can shift the duty point.
Importance of the Pump Duty Point
Optimal Efficiency
Operating at the pump duty point ensures the pump runs at its most efficient level, minimizing energy consumption and operating costs.
Proper Sizing
Knowing the duty point helps select the right pump size to match system requirements, avoiding under or over sizing.
Reliability
Running a pump at the duty point reduces stress on the equipment and extends its lifespan, improving overall reliability.
System Performance
Maintaining the pump at the duty point optimizes the entire system’s performance, ensuring consistent and reliable operation.
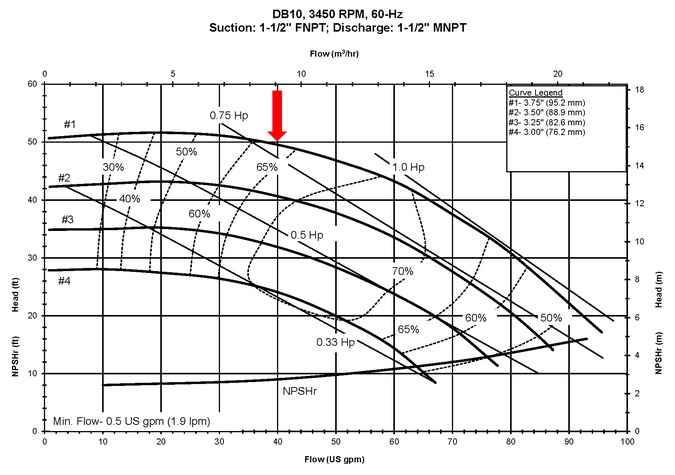
Determining the Pump Duty Point
System Curve
Analyse the system resistance curve to determine the required flow rate and pressure.
Pump Curve
Match the system requirements to the pump’s performance curve to identify the duty point.
Verification
Confirm the duty point through field testing or simulation to ensure optimal pump operation.
Optimizing the Pump Duty Point
Adjust Impeller
Trimming or replacing the impeller can shift the pump’s performance curve to match the duty point.
Throttle Valves
Strategically throttling valves can modify the system resistance curve to align with the pump’s performance.
Adjust Speed
Varying the pump’s speed can also move the duty point to the desired operating condition.
Regular Maintenance
Maintaining the pump and system components helps preserve the optimal duty point over time.
Practical Applications of the Pump Duty Point
Industrial Processes
Ensuring consistent flow and pressure for manufacturing, chemical, and power generation applications.
Water Treatment
Optimizing pump performance to efficiently move and treat water and wastewater.
HVAC Systems
Designing and operating circulating pumps at the duty point for heating, cooling, and ventilation.
Irrigation and Agriculture
Selecting the right pump to meet crop irrigation and water distribution needs.